Do you know?
- World Pneumonia Day is an event that is observed every year on 12th November to spread awareness and educate people to deal with it.
- The slogan of World Pneumonia Day is “Pneumonia affects everyone”.
- The word “pneumonia” originates from the Ancient Greek word “pneumon”, which means “lung”.
- It is the leading infectious cause of death in children worldwide. Every year, it kills more than 700,000 children under the age of 5, including more than 153,000 newborns.
Pneumonia is a common lung infection that causes inflammation and fluid accumulation in the air sacs of the lungs, also called alveoli, making it hard to breathe. It can cause symptoms like cough, fever, chills, and difficulty in breathing.
There are different types and causes of pneumonia one of them is multifocal pneumonia.
What is multifocal pneumonia?
It is a type of pneumonia that affects more than one area of the lungs. Unlike pneumonia, which usually affects one lobe of the lung, it can affect multiple lobes or even both lungs. This makes it more difficult to diagnose and treat because the symptoms can be more severe and widespread.
Symptoms of multifocal pneumonia
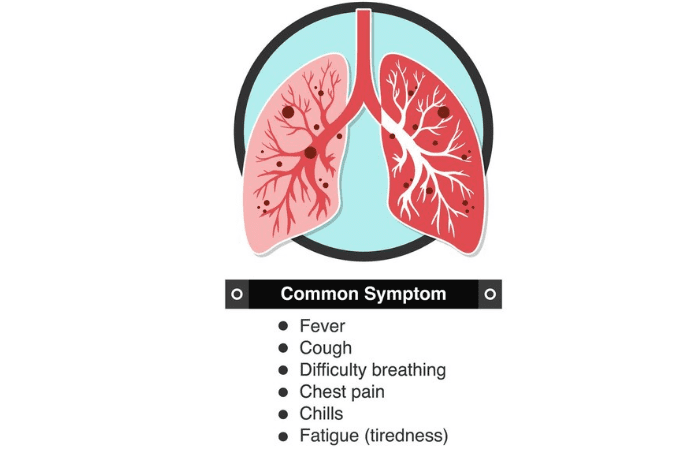
Symptoms are similar to other types of pneumonia. Signs may vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection.
Some common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Feeling cold
- Coughing up mucus or blood
- Chest pain or tightness
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Fatigue or weakness
- Loss of appetite or weight loss
- Confusion or delirium
However, it may also have some specific features, such as:
- Spotty areas of swelling and fluid in the lungs, that can be seen on a chest X-ray.
- Rapid onset and progression of symptoms.
- Higher risk of complications and mortality.
Related: Necrotizing Pneumonia Prognosis That You Need To Know
Causes of multifocal pneumonia
According to experts, this variety of pneumonia is more likely to be caused by viruses than other types of pathogens such as bacteria, or fungi.
Some of the reasons are:
1. Viruses:
It can be caused by viral infections, especially in people with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
Some common viral causes include:
- 1. COVID-19
- 2. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- 3. Influenza
2. Bacteria:
Bacterial infections can also cause multifocal pneumonia, especially if they are not treated promptly or adequately.
Some of the bacteria that can cause multifocal pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydia pneumoniae.
3. Fungi:
Fungal infections are less common causes of multifocal pneumonia. They can occur in people with weakened immune systems or underlying lung diseases ( people with HIV/AIDS or other immunosuppressed conditions).
Some of the fungi that can cause multifocal pneumonia are Pneumocystis jiroveci, Coccidioides immitis, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Histoplasma capsulatum.
Is multifocal pneumonia dangerous?
It is not dangerous. But when left untreated it can lead to complications such as:
- Lung abscess: This is a condition that occurs when a pocket of pus forms in your lung due to the infection. It can cause symptoms such as chest pain, coughing up blood, weight loss, or fever.
- Pleural effusion: This is a condition that occurs when fluid builds up in the space between your lung and chest wall due to an infection or inflammation. It can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, cough, or fever.
- Empyema: This is a condition that occurs when pus accumulates in the space between your lung and chest wall due to the infection. It can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fever, or cough.
- Sepsis: This is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads from your lungs to your bloodstream and other organs. It can cause symptoms such as fever, chills, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, organ failure, or death.
- Respiratory failure: This is a life-threatening condition that occurs when your lungs cannot provide enough oxygen to your body or remove enough carbon dioxide from your blood. It can cause symptoms such as confusion, agitation, coma, or death.
- Lung scarring or fibrosis: This condition causes scar tissue to build up in the lungs, which can reduce their function and elasticity.
Multifocal pneumonia may also increase the risk of developing chronic lung diseases such as asthma or COPD. Therefore, if you suspect that you have multifocal pneumonia or any other type of pneumonia, it is important to seek medical help.
How is multifocal pneumonia diagnosed?

To diagnose it your doctor will ask you about your symptoms, medical history, and potential exposure to infectious agents. They will also examine your lungs with a stethoscope and check your vital signs, such as your temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation.
To confirm the diagnosis and identify the cause of the infection, your doctor may order certain tests such as:
- Chest X-ray or CT scan: These imaging tests can show the extent and location of damage to the lungs caused by multifocal pneumonia.
- Blood tests: These tests can measure your white blood cell count, inflammation markers, and oxygen levels. They can also detect specific antibodies or antigens associated with the infection.
- Sputum culture: This test involves taking a sample of your mucus and sending it to a laboratory for analysis. It can help identify the specific microorganism causing your multifocal pneumonia and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Bronchoscopy: This test involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into your airways to examine your lungs and collect samples for testing. It can help diagnose multifocal pneumonia caused by fungi or other rare organisms.
Multifocal pneumonia treatment
The treatment depends on the cause and severity of the infection.
Some common treatments include:
1. Antibiotics.
These medicines are used to treat bacterial infections. They are usually given intravenously (through a vein) in the hospital until you improve. The type and duration depend on the specific bacteria causing your infection.
2. Antiviral.
These drugs are used for the treatment of viral infections. They can be given orally or intravenously, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
3. Antifungal.
These medicines are used to treat fungal infections. They are usually given orally or intravenously in the hospital or at home. The type and duration depend on the specific fungus causing your infection and its sensitivity to antifungals.
4. Oxygen therapy.
This treatment involves delivering oxygen to your lungs through a mask or a tube in your nose. It can help improve your breathing and oxygen levels in your blood.
5. Fluids and electrolytes.
These treatments involve giving you fluids and minerals through a vein or by mouth. They can help prevent dehydration and correct any imbalances in your blood.
6. Pain relievers and fever reducers.
These drugs can help ease your chest pain and lower your fever. They include acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
You should avoid aspirin if you have viral multifocal pneumonia, as it can increase the risk of bleeding.
7. Cough suppressants.
These drugs can help reduce your cough and loosen the mucus in your lungs. They include dextromethorphan, guaifenesin, or codeine. You should use them with caution, as they can make you drowsy or interfere with your breathing.
8. Breathing exercises.
These treatments involve performing certain breathing techniques and movements to help clear the mucus from your lungs and improve your lung function. They may be done by yourself or with the help of a physical therapist or a respiratory therapist.
In some cases, you may need more intensive treatment for multifocal pneumonia, such as:
1. Mechanical ventilation.
This treatment involves using a machine to help you breathe when your lungs are too weak or damaged. It requires inserting a tube into your mouth or nose and connecting it to a ventilator that delivers oxygen and air pressure to your lungs.
2. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
This treatment involves using a machine to pump and oxygenate your blood outside your body when your lungs and heart are too weak or damaged. It requires inserting tubes into your veins and arteries and connecting them to an ECMO machine that acts as an artificial lung and heart.
3. Surgery.
This treatment involves removing part of your lung that is severely infected or damaged by multifocal pneumonia. It is usually done as a last resort when other treatments fail or cause serious complications.
How long does multifocal pneumonia last?
It can take several weeks to months to fully recover from multifocal pneumonia. The exact duration can be determined as it varies depending on the cause and severity of the infection.
How it can be prevented?
The best way to prevent multifocal pneumonia is to avoid getting infected by the microorganisms that cause it.
Some of the preventive measures are:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizer
- Avoid contact with people who have respiratory infections or symptoms.
- Wear a mask or cover the nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing.
- Get vaccinated against influenza, pneumococcal pneumonia, and COVID-19.
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Limit alcohol intake and eat a balanced diet.
- Drink plenty of fluids and stay hydrated.
- Exercise regularly and do breathing exercises.
Multifocal pneumonia is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. If you have symptoms of pneumonia, especially if you have a high fever, chest pain, or difficulty breathing, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.


Hey, cool post You can check if there’s a problem with your website with Internet Explorer. Because of this issue, many readers will overlook your excellent writing because IE is still the most popular browser.
Can you share the screenshot, because we don’t find such issue in internet explorer.